Cracking the code of human behavior: What really works?6 min read
Reading Time: 5 minutesReading Time: 5 minutesOver the past five years, humanity has faced some pretty tough problems like pandemics, climate threats, and violence. These significant social, environmental, political, and economic challenges need smart solutions. Scientists looked at different things that make us act a certain way, like what we know, how we feel, and what we believe, and figured out which ones are the best to focus on for making changes. Do people have the capacity to transform human behavior?
The study Determinants of behaviour and their efficacy as targets of behavioural change interventions synthesizes research to guide decisions on behavioral change targets, summarizing meta-analytic evidence on correlations between determinants and behaviors and the effectiveness of various interventions. This study aims to create a model based on solid evidence to guide strategies for new or not well-understood behaviors. The focus is finding the most effective ways to bring about positive change and tackle these crises. The research by Dolores Albarracin, Bita Fayaz-Farkhad, and Javier A. Granados Samayoa outlines factors influencing behavior, their definitions, measurement methods, and strategies.
The Behavior Change Puzzle
The methodology is underpinned by theories such as the reasoned action approach, social cognitive theory, and the information-motivation-behavioral-skills model, ensuring a robust theoretical framework. By synthesizing findings from numerous individual studies through meta-analyses, the researchers provide a statistical approach to combining the results of multiple studies. Authors categorized interventions into individual (e.g., knowledge, beliefs, attitudes) and social-structural determinants (e.g., social norms, material incentives, institutional trustworthiness). This practical approach allowed for a clear understanding of which interventions are most effective.
Overall, while individual determinants focus on personal attributes and internal processes, social-structural determinants involve external influences and contextual factors that can significantly shape behavior. The study highlights that interventions targeting social-structural determinants have a larger and more sustained impact on behavior change than those targeting individual determinants.
Did we always get it wrong?
The study found that some strategies work better than others, because they address the personal and contextual factors that influence behavior, making it easier for individuals to adopt and maintain positive changes. Coming in strong are interventions that focus on behavioral skills and attitudes.
Individual Determinants
1. Boosting Behavioral Skills
It’s all about building the confidence and know-how to tackle tasks like effective communication and time management. Think of it as giving yourself the tools to turn intentions into actions. Confident people are more likely to stick with their goals, and that’s why these skills matter so much.
To level up, immerse yourself in practical training, engage in role-playing, and soak up feedback. Imagine attending a workshop that teaches you how to communicate better — it can make all the difference in discussing health behaviors with your family. It’s all about practice making perfect!
2. Shaping Behavioral Attitudes
Attitudes towards behaviors like exercising or recycling are all about how positively or negatively you feel about these activities, usually measured by favorability scales. These feelings are super important because they directly influence whether you’ll actually do the behavior. If you feel good about something, you’re way more likely to do it.
To level up, tackle these attitudes with cool interventions like media campaigns highlighting the benefits or motivational talks addressing common hurdles. Imagine a recycling campaign that shows how it helps the environment and your community — it can totally shift your mindset and get you recycling more.
3. Harnessing the Power of Emotions
Emotions, often measured by how strongly you agree or disagree with specific statements about your feelings, significantly motivate behavior change. For instance, people experiencing anxiety about COVID-19 have increased their protective behaviors, and even though perceived climate change risk shows only a small correlation with adaptation behaviors, the impact remains notable.
To level up, combine emotional appeals with practical support, making emotions a powerful tool for influencing actions.
Social-structural determinants
By focusing on these social-structural determinants, interventions can create an environment that supports and sustains positive behavior changes, ultimately leading to healthier and more engaged communities.
1. Increasing Access
It involves removing barriers that prevent individuals from performing desired behaviors. This can include providing resources, facilities, or opportunities that make it easier for people to engage in positive actions.
To level up, strategic planning to identify and eliminate obstacles is essential. Remove barriers and make it easier for individuals to engage in desired behaviors. For example, a company could provide remote work options to increase access to flexible working conditions, improving employee satisfaction and productivity.
2. Providing Social Support
It encompasses the informational, emotional, and practical assistance others provide to help individuals perform specific behaviors. This support can come from family, friends, or community groups.
To level up, people should create environments where they can share experiences and encouragement. Imagine joining a professional networking group where members exchange business strategies, celebrate career milestones, and provide encouragement. This collective effort fosters a supportive environment, making it easier to stay committed to professional development goals.
3. Offering Material Incentives
Material incentives provide tangible rewards for engaging in positive behaviors. These incentives can range from financial rewards to other benefits that motivate individuals to adopt and sustain desired behaviors.
To level up, aligning the rewards with the behavior can drive better outcomes. Consider a company offering bonuses for employees who achieve wellness goals, such as regular exercise or smoking cessation. This direct linkage between incentives and behavior fosters a culture of health and wellness.
Take a closer look at these three circular diagrams that illustrate the effectiveness of various interventions on human behavior:
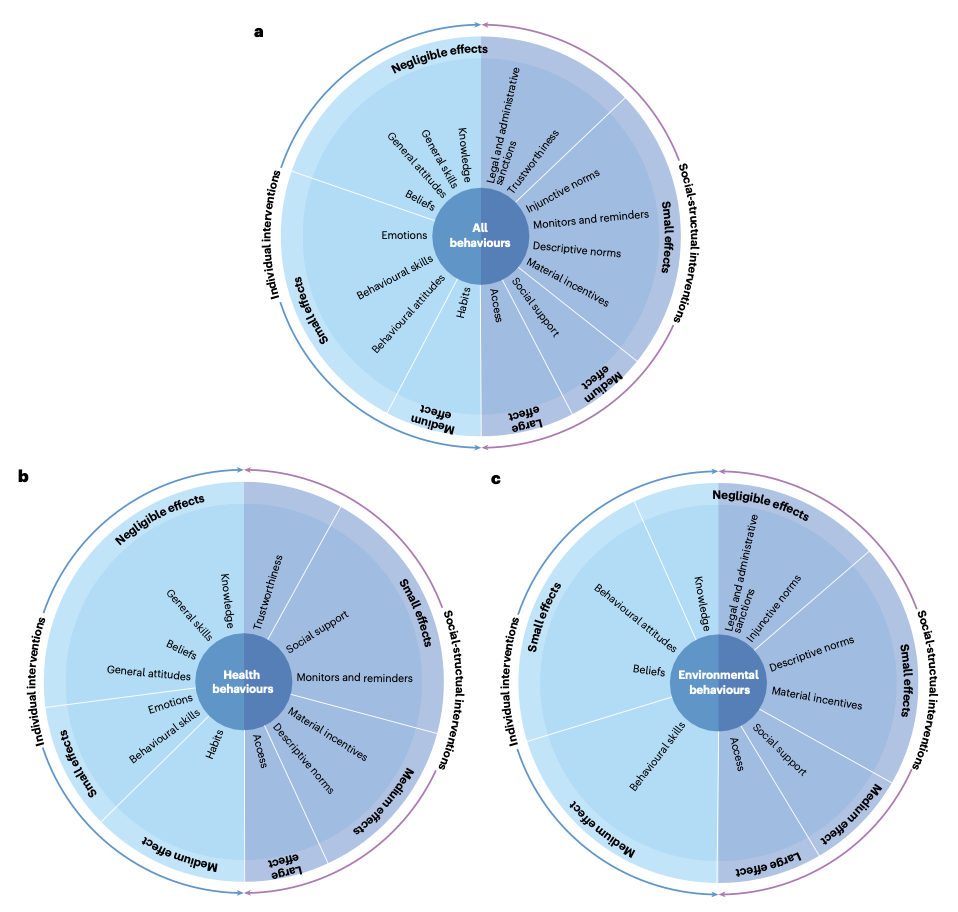
The first diagram covers all behaviors, showing how different individual and social-structural interventions can range from negligible to large effects. The second focuses specifically on health behaviors, while the third addresses environmental behaviors. Explore these diagrams to gain more insights into what types of interventions are most effective.
AI’s Behavioral Makeover
AI could be a powerful tool for behavior change by providing personalized, real-time feedback and guidance tailored to an individual’s goals and challenges. By leveraging machine learning algorithms to analyze patterns in a person’s habits, AI could offer timely interventions, adaptive strategies, and constant support, making adopting new behaviors more effective and sustainable than traditional methods.
The influence of AI on behavior change is becoming increasingly apparent in both educational and professional spheres. In colleges, AI is dramatically altering study habits and academic strategies. Over half of students report improved grades and efficiency thanks to AI tools, which they’re using for basic tasks like proofreading and more complex processes such as problem-solving and creating study materials. This shift is changing how students approach learning, pushing them towards more tech-integrated study methods. However, this behavioral change creates tension with faculty members less prepared to incorporate AI into their teaching methods, leading to a notable divide in the academic ecosystem.
In the professional realm, AI reshapes how individuals approach skill development and career growth. LinkedIn’s AI-powered coaching, lauded by 76% of users for enhancing their skill development, is a prime example of how AI influences professional behavior. By providing personalized, real-time advice tailored to specific career goals and skill needs, this tool encourages professionals to adopt more proactive and targeted approaches to learning. As AI transforms the job market, it’s also driving a behavioral shift towards continuous, AI-guided learning and adaptation. This trend underscores how AI is changing what we learn and fundamentally altering how we approach education and career development, nudging students and professionals towards more efficient, personalized, and technology-driven paths to success.
Conclusion
From tackling global challenges to reshaping educational and professional environments, AI integration is proving to be a game-changer. By leveraging AI’s capabilities for personalized feedback, real-time interventions, and adaptive learning strategies, we can enhance the effectiveness of both individual and social-structural approaches to behavior change. As we navigate complex societal issues, the synergy between traditional behavior change methods and AI-driven solutions offers a promising path forward.




